Climate characteristics
 Bosnia and Herzegovina has the temperate continental climate type, which is represented mostly in the northern and central parts of BiH; the sub-mountainous and mountainous type (over 1000 m) and the Adriatic (Mediterranean) and modified Adriatic climate type, which represented in coastal area of Neum and includes the Herzegovinian lowlands. The climate of Bosnia and Herzegovina therefore varies from a temperate continental climate in the northern Pannonia lowlands along the Sava River and in the foothill zone, to an alpine climate in the mountain regions, and a Mediterranean climate in the coastal and lowland areas of the Herzegovina region in the south and southeast. In the northern part of the country, air temperature generally ranges between -1 and -2°C in January and between 18 and 20°C in July. In highlands with the altitude above 1000 m, the average temperature ranges from -4 to -7°C in January to 9 to 14°C in July. On the Adriatic coast and in the lowland regions of Herzegovina, air temperature ranges from 3 to 9°C in January to 22 to 25°C in July (for the period 1961-1990). Extremes of -41.8°C (low) and 42.2°C (high) have been recorded.
Bosnia and Herzegovina has the temperate continental climate type, which is represented mostly in the northern and central parts of BiH; the sub-mountainous and mountainous type (over 1000 m) and the Adriatic (Mediterranean) and modified Adriatic climate type, which represented in coastal area of Neum and includes the Herzegovinian lowlands. The climate of Bosnia and Herzegovina therefore varies from a temperate continental climate in the northern Pannonia lowlands along the Sava River and in the foothill zone, to an alpine climate in the mountain regions, and a Mediterranean climate in the coastal and lowland areas of the Herzegovina region in the south and southeast. In the northern part of the country, air temperature generally ranges between -1 and -2°C in January and between 18 and 20°C in July. In highlands with the altitude above 1000 m, the average temperature ranges from -4 to -7°C in January to 9 to 14°C in July. On the Adriatic coast and in the lowland regions of Herzegovina, air temperature ranges from 3 to 9°C in January to 22 to 25°C in July (for the period 1961-1990). Extremes of -41.8°C (low) and 42.2°C (high) have been recorded.
The lowland area of northern Bosnia and Herzegovina has a mean annual temperature of between 10°C and 12°C, and in areas above 500 m the temperature is below 10°C. Mean annual air temperature in the coastal area ranges between 12°C and 17°C. In the period 1981-2010, an increase in air temperature was recorded in the entire territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The highest increase of approximately 1°C is recorded during summer and winter period.
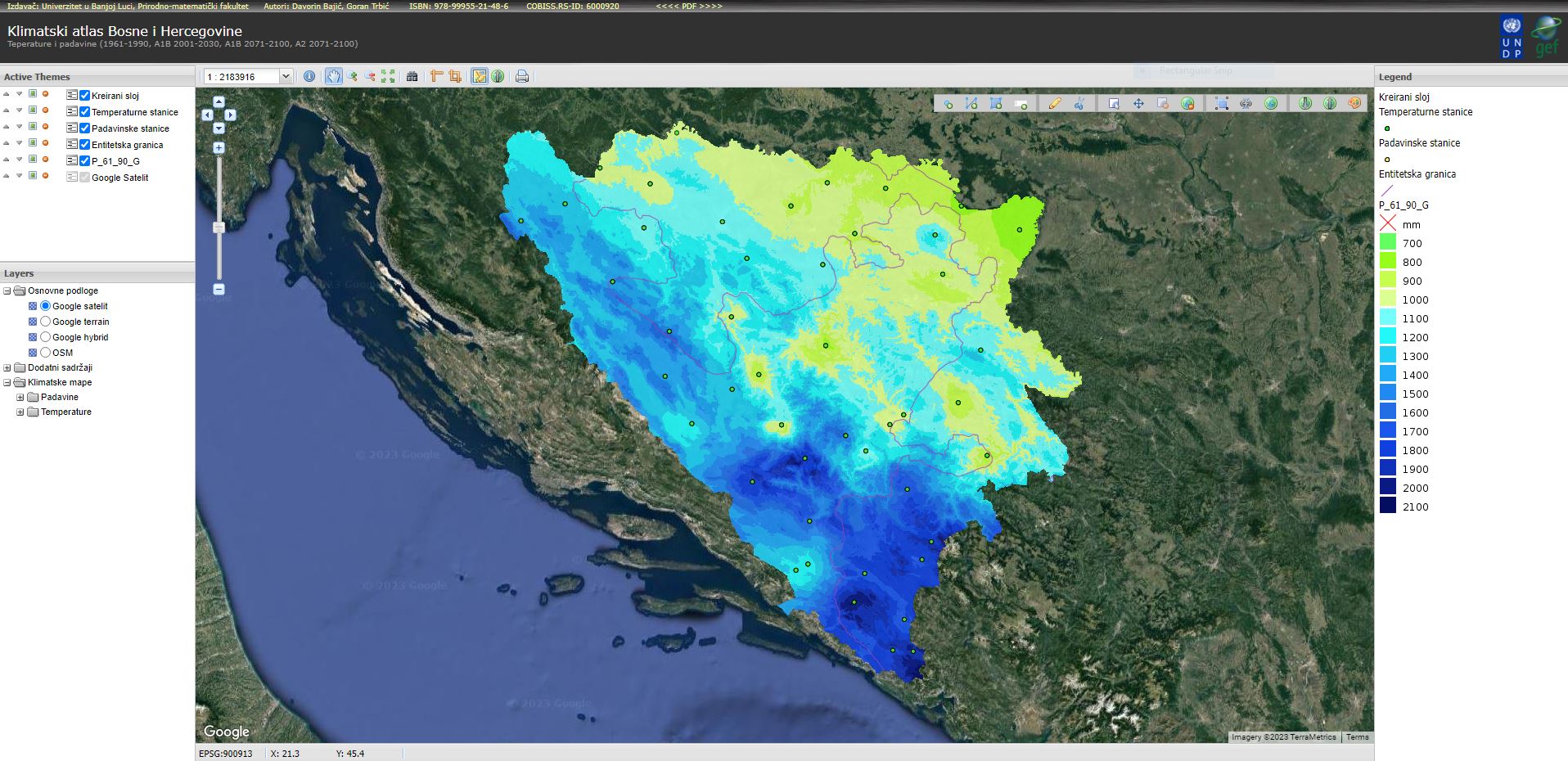
Annual precipitation amounts range from 800 mm in the north along the Sava River to 2000 mm in the central and southeastern mountainous regions of the country (period 1961-1990). In the continental part of BiH belonging to the Danube River catchment area, a major part of annual precipitation occurs in the warmer half of the year, reaching its maximum in June. The central and southern part of the country with numerous mountains and narrow coastal regions is characterized by a maritime pluviometric regime under the influence of the Mediterranean Sea, so the monthly maximum amounts of precipitation are reached in late autumn and at the beginning of the winter, mostly in November and December. During the period 1981-2010, major parts of the Herzegovinian lowlands saw a decrease in annual precipitation, whereas the majority of mountainous meteorological stations recorded an increase in precipitation. Compared to 1961-1990, this period had a more uneven distribution of precipitation throughout, which was one of the main factors causing more frequent droughts and flooding.
The duration of sunshine decreases from the sea towards the mainland and at higher altitudes. Annual duration of sunshine in the central mountainous area is 1700-1900 hours, as a consequence of the above average cloudiest conditions (60-70%). Due to frequent fogs during the cold part of the year, solar irradiation inland is lower than at the same altitudes in the coastal area. In southern regions, there are 1900-2300 hours of sunshine (Mostar = 2285 hours). In northern Bosnia and Herzegovina, there are 1800-2000 hours of sunshine, more in the eastern part than in the western part. Cloudiness declines from the west to the east.
Average annual precipitation in BiH is about 1,250 mm, which -- given that the surface area of BiH is 51,209 km2 -- amounts to 64 x 109 m3 of water, or 2,030 m3/s. The outflow from the territory of BiH is 1,155 m3/s, or 57% of total precipitation. However, these volumes of water are not evenly distributed, either spatially or temporally. For example, the average annual outflow from the Sava River basin, which has a surface area of 38,719 km2 (75.7%) in BiH, amounts to 722 m3/s, or 62.5%, while the outflow from the Adriatic Sea basin, which has a surface area of 12,410 km2 (24.3%) in BiH, is 433 m3/s, or 37.5%.